What is corporate strategy? Simply a well-defined long-term portfolio approach set by an organisation after analysing their business carefully. Its main purpose is to create maximum corporate value while motivating their workforce to implement the right actions to win customer satisfaction.
Companies that want to provide customer value successfully must go back regularly to their corporate strategy as it helps them improve in various areas likely to hinder their goals and accomplishments.
In today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape, organizations face the challenge of formulating and implementing effective strategies to achieve sustainable growth and success. At the heart of this strategic endeavor lies the distinction between corporate strategy and business unit strategy. While corporate strategy provides the overarching framework and direction for the entire organization, business unit strategy delves into the specific plans and actions required for each business unit or product line. Understanding the nuances of these two strategic levels is crucial for businesses to effectively allocate resources, align initiatives, and achieve their desired outcomes.
Corporate strategy, often referred to as the “grand strategy,” encompasses the organization’s overall mission, vision, and goals. It outlines the long-term direction of the company, defining how it will position itself in the market and compete against its rivals. Corporate strategy typically encompasses decisions such as diversification, acquisitions, and resource allocation across the entire organization.
On the other hand, business unit strategy takes a more granular approach, focusing on the specific strategies and tactics required for each business unit or product line. It considers the unique competitive landscape, customer needs, and operational challenges faced by each unit, crafting a tailored plan to achieve its objectives. Business unit strategy typically encompasses decisions such as product development, marketing campaigns, and sales strategies.

While corporate strategy provides the overarching framework, it is business unit strategy that translates this vision into actionable plans and drives day-to-day operations. Effective business unit strategies must align with the corporate strategy, ensuring that the organization’s overall goals are consistently pursued across all units.
Table of Contents
What is Corporate Strategy? Three Steps for Positive Results
A company aiming to develop a corporate strategy with positive results must focus on three things:
1. Develop a Clear Vision
Create and share a long-term vision to keep their team motivated while engaging investors. Think of where you want to be in the next five to ten years. This might be in terms of profit, number of employees, geography or industry.
For example, you might want to move into an entirely new market. Alternatively, you might want to increase your annual profits by a specific percentage.
2. Approach Definition
This ensures that your strategy defines how to achieve the vision. Think about areas of investment you need to venture and areas to expand. Remember to establish a corporate process and policies that reflect the nurturing approach by your company.
It’s vital to set the right goals for your corporate strategy. You can use the SMART framework to ensure this. Your goals should be:
- Specific,
- Measurable,
- Achievable,
- Relevant,
- Timely.
3. Make Your Corporate Strategy a Continuous Strategy
A company must make their corporate strategy an on-going strategy. Keep offering value creation, which is too fast to your competitors. They will regularly go back to the drawing board to renew their strategies.
Once you’ve got a clear picture of what you’d like to achieve with your corporate strategy, this is naturally much easier. The remaining step is to have the right procedures in place to measure your progress over time.
What to Consider When Applying Corporate-Level Strategy
Of course, creating a corporate strategy is much more complicated than thinking about your day to day operations. In fact, there are a few additional things you’ll need to keep in mind when strategizing for an entire corporation.
Long-Term Objectives
The strategic plan should have long term and specific objectives. Think about the services or products you would want to make and identify your targeted customers. Think about the markets to supply and activities you would enjoy being part of.
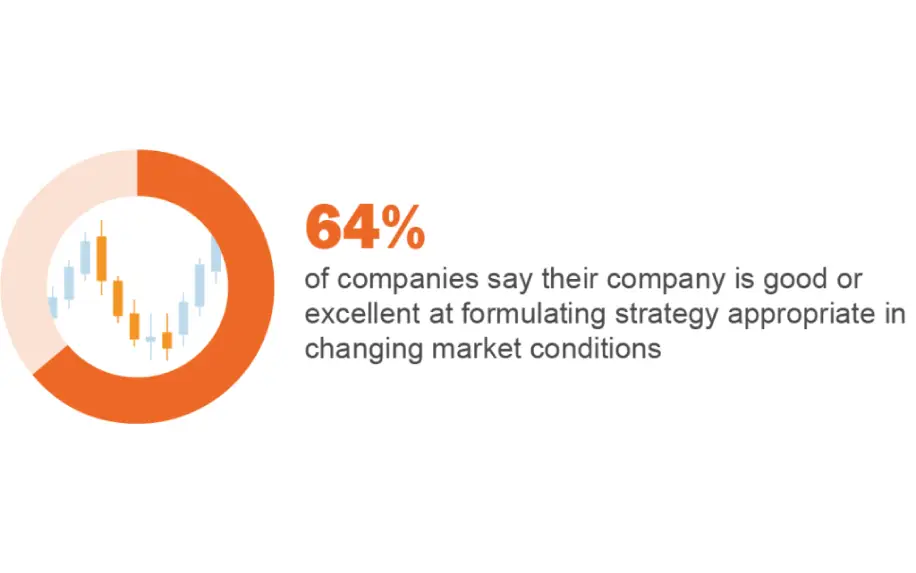
This becomes tricky in the corporate world, as you’re potentially dealing with the livelihoods of hundreds of people.
Additionally, since many corporations operate across borders, there are many variables to take into account. Often, it’s simply impossible to predict the future in your corporate strategy.
Opportunity
Take time to analyse the opportunities available and how they might change with time. Get a lot of information and facts about possible developments before you make the final decision.
Weigh the challenges and risks anticipated in your journey and come up with solutions in advance.
Innovation
Make sure your services or products are unique with a clear differentiation that can only be aligned with your company. It is not easy, but attainable with proper strategies. This is about brand creation. A good example is Apple’s iPhone.
Since they created this product, no one has matched their quality. So people buy their products despite the high prices.
Competition
The corporate strategy you choose must always remain competitive. Go for a market that is in need. It could be underserved or not served at all. This means you lead from the beginning because competition is very little or there is none.
You are able to capture the market before others discover it and position your business. You can build a brand in that industry making it hard for new entrants to get into the field.
Economies of Scale
Be innovative but lower the price of your services or goods. Include high quality services to customers and some unique features. A good example is how Wal-Mart (Asda in the UK) has low prices but makes huge sales therefore making higher profits than most stores with highly priced products.
Time to Market
Carefully weigh between building and buying services or products you plan to sell. See which is cheaper and profitable. Is it buying or creating the solutions? You can outsource some of these services or buy products and save on cost.
Tests
Keep updating and reviewing your strategy periodically to make sure that it’s still effective. Test it in small phases. You will know if it’s valid and good enough for your firm’s market needs and objectives.
Risks Undertaken and Possible Failures
Identify risks in your plan and learn from them by coming with a solution beforehand. Allow your firm to accept and move on beyond failures using insights acquired from failures and successes from your past.
Use any positive or negative experience as knowledge to improve the future.
Stakeholders
After completing the plan, share and reason with your company’s employees on how to implement it. Guide them and provide them with information on the various initiatives to be carried out in the business.
Let them understand its relationship to the firm and all employees.
However, do not forget about external shareholders including suppliers, customers, industry analysts, partners and investors. Explain to them what it means, reasons behind it, and how it will change revenue generation and impact the value of shareholders.
Examples of Corporate Strategy
Every business has its mission. Therefore, it has to create business strategies designed to offer support to its specific goal, value and vision in its industry, market and business.
As a company or an organization, it’s prudent to take time to understand and analyse the market, external environment and the industry as whole to come up with strategies that will boost your company’s success.
What is Corporate Strategy? The ‘Why’ of Corporate Strategy
So what is the point of creating a corporate strategy? Ultimately, it comes down to achieving your goals more effectively. The stronger your long term planning, the more you’ll be able to succeed in business.
Here are a few of the key benefits you can expect from corporate strategy.
Growth
This is a strategy that a company applies to expand in various markets to offer services or sell their products through new business or current business. Growth strategy may require a company to hire more employees, increase their market or revenues.
They grow by applying concentration, diversification, vertical integration or horizontal integration.
Diversification is a strategy that tries to boost profitability of an organization by increasing sales of new products or services in a new market. Both vertical and horizontal integration refers to the process of acquisition or merging with other companies in the same industry.
Stability
A stable strategy means a company does not change doing its current business. They maintain their market share and sell the same services or products. This strategy is intended to help a business maintain its position and their focus is incremental improvement.
This involves changing the business operations either collectively or individually in customer functions, technology alternatives or customer groups.
Stability strategy is used by companies that do not find market conditions favourable to them.
They choose not to make any major changes in their business operations. The organization remains stable and safe with the stability strategy and will not seek any different options.
Renewal
The corporate renewal strategy is also known as a turnaround strategy. It’s always an emergency response to a firm’s poor performance. The managers must apply strategies to address the declining performance of a business.
If the sales are low or the company has to meet unexpected expenses or costs, a strategy to alleviate the problem can be created. Here are several ways to use the renewal corporate strategy:
Timing
The corporate can be used before a company gets into deep trouble such as bankruptcy. There are different options that can help prevent negative events from occurring and ruining a business.
Timing is important because if the management takes a loan while the business is still on its feet and profitable, they can easily appeal to new stakeholders and it will be renewed on time.
Division Analysis
For a corporation with numerous divisions, renewal strategy considers each division’s future profitability and fixes any problems experienced by a division that has the potential to make high profits in the forthcoming days.
Unprofitable divisions without a bright future can be sold off, or closed down.
Remember though, when you close down an entire division, you have obligations to make a reasonable effort to redeploy the staff.
Implementation Problems
In some companies, it is hard to implement the turnaround strategy. A good example is a manufacturing company with broken equipment. No matter how high the costs are, they must pay for them to keep the business running.
Other industries have it easier like a software company can save on office expenses by hiring people online. They do not need to rent an office in every country where they want to sell their products and services.
Company Purpose
Sometimes the corporate renewal may bring a change on the firm’s main business. For example, if the costs of manufacturing are too high, a company can decide to import ready products from a country where they are cheaper.
Or a newspaper can move from hardcopy to softcopy. It can also include buying a competitor with popular products or useful patents. All these can help reduce production costs and increase profit.
Products
A firm can use corporate renewal to change their product lines. A good example is targeting the wrong audience. So they try out new demographics and reach many customers. Redesigning a product or changing its packaging can also increase sales. These are just a few, more can be done.
What is Corporate Strategy? The Benefits of Corporate Strategy
A corporate strategy not only states the intended outcome, but also devises credible means to achieve these goals. The strategy determines a firm’s scope of activities and the way its business processes back the firm’s goals.
A corporate strategy helps to improve a firm’s competitive position, its expectations and resources while increasing shareholder value to an amount more than its physical assets.
Company Resource Allocation
A company can use a corporate strategy to limit its resources allocation to the best available investment opportunities. The performance of every business unit is assessed during budget and strategic planning processes.
They may revise resource allocation or acquire assets based on the assessment results. Each business unit is allocated funds according to its market opportunities.
Establishing Expectations
The corporate strategy is conveyed to business units to enhance performance and establish the expectations of external and internal stakeholders.
The objectives focus mainly on profitability, productivity and market standing under which the company sets measurable objectives including attaining a specific amount in return on investments and market share.
The established expectations help stakeholders to align activities with strategic goals and lead in some roles until the corporate strategy is successful.
Improvement and Competitive Positioning
The corporate strategy checks on the business profit and growth performance. It helps to improve a firm’s competitive position by managing and structuring the business units.
Corporate Strategy varies from business to another and its main focus is to manage risk, resources and return. After all, managers will only succeed if they consider all factors before making any strategic decisions.
It’s evident that strategy is paramount in every business to meet its goals and objectives. Although the types of strategy may differ, results are the same; to enhance customer satisfaction, grow the business and achieve set goals.
Key components of corporate strategy:
Positioning
Positioning is a crucial element of corporate strategy that involves establishing a distinctive place in the market for a company’s products or services. It’s about crafting a clear and compelling perception of the brand in the minds of target customers, differentiating it from competitors and securing a loyal customer base.
Key Aspects of Positioning:
- Target Market Identification: Clearly define the specific group of consumers the company aims to serve.
- Competitive Analysis: Thoroughly understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats posed by competitors.
- Unique Value Proposition: Articulate what sets the company apart, emphasizing the distinct benefits and advantages it offers to customers.
- Consistent Communication: Effectively convey the positioning message across all marketing channels, ensuring a cohesive brand image.
Examples of Effective Positioning:
Red Bull: Positioned as an energy drink that boosts mental and physical performance, appealing to active individuals and athletes.
- Key elements of Red Bull’s positioning:
- Emphasis on energy and vitality
- Association with extreme sports and adventure
- Targeted messaging for athletes and fitness enthusiasts
Apple: Positioned as a premium technology brand that offers innovative and user-friendly products, resonating with consumers seeking high-quality tech experiences.
- Key elements of Apple’s positioning:
- Focus on design and aesthetics
- Emphasis on user experience and simplicity
- Aspirational branding and marketing
Nike: Positioned as a leading athletic apparel and footwear brand that inspires and empowers athletes of all levels.
- Key elements of Nike’s positioning:
- Association with sports stars and athletic excellence
- Emphasis on performance and innovation
- Motivational messaging that connects with athletes’ aspirations
Harley-Davidson: Positioned as an iconic motorcycle brand that represents freedom, rebellion, and individuality.
- Key elements of Harley-Davidson’s positioning:
- Heritage and authenticity
- Association with the open road and adventure
- Emotional appeal to a passionate customer base
Tiffany & Co.: Positioned as a luxury jewelry brand that represents elegance, romance, and timeless style.
- Key elements of Tiffany & Co.’s positioning:
- Emphasis on craftsmanship and quality
- Association with luxury and sophistication
- Targeted marketing to affluent consumers
Compilation of statistics highlighting the impact of effective corporate strategies on the performance of top companies:
- Apple’s market capitalization surpassed $3 trillion in 2022, demonstrating the remarkable growth driven by its strategic focus on innovation, user experience, and premium positioning.
- Amazon’s revenue reached $470 billion in 2022, reflecting the success of its strategic expansion into cloud computing, e-commerce, and digital advertising.
- Alphabet (Google’s parent company) generated $257 billion in revenue in 2022, showcasing the effectiveness of its strategic investments in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and self-driving cars.
- Microsoft’s revenue reached $168 billion in 2022, highlighting the impact of its strategic pivot to cloud computing and productivity software.
- Tesla’s market capitalization surged to over $1 trillion in 2021, driven by its disruptive approach to electric vehicles and autonomous driving technology.
Comparison of corporate strategy and business unit strategy:
| Feature | Corporate Strategy | Business Unit Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broader, encompassing the entire organization | Narrower, focused on a specific business unit or product line |
| Focus | Defines the overall direction and objectives of the organization | Defines the specific strategies and tactics for a particular business unit |
| Time Horizon | Long-term, typically spanning 3-5 years or more | Medium-term, typically spanning 2-3 years |
| Decision-Making | Made by senior executives | Made by business unit managers |
| Alignment | Business unit strategies must align with the corporate strategy | Corporate strategy provides a framework for business unit strategies |
Examples of Corporate Strategy:
- Apple’s strategy of focusing on innovation, user experience, and premium positioning has driven its remarkable growth and market dominance.
- Amazon’s strategy of expanding into cloud computing, e-commerce, and digital advertising has transformed it into a leading technology and retail giant.
- Alphabet’s strategy of investing in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and self-driving cars has positioned it for long-term growth and innovation.
Examples of Business Unit Strategy:
- Nike’s strategy in its footwear business unit focuses on performance innovation, athlete partnerships, and targeted marketing to specific sports categories.
- Procter & Gamble’s strategy in its beauty care business unit focuses on developing innovative products, acquiring complementary brands, and expanding into emerging markets.
- Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) strategy focuses on providing a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services, attracting enterprise customers, and expanding into new geographic markets.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Corporate strategy takes a holistic view of the entire organization, while business unit strategy focuses on a specific area of the business.
- Focus: Corporate strategy defines the overall direction and objectives, while business unit strategy outlines specific plans and actions.
- Time Horizon: Corporate strategy has a long-term perspective, while business unit strategy has a medium-term focus.
- Decision-Making: Corporate strategy decisions are made by senior executives, while business unit strategy decisions are made by business unit managers.
- Alignment: Business unit strategies must align with the corporate strategy to ensure coherence and overall success.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between corporate strategy and business unit strategy?
A: Corporate strategy defines the overall direction and objectives of the entire organization, while business unit strategy outlines the specific plans and actions for a particular business unit or product line.
Q: What are the key elements of corporate strategy?
A: Key elements of corporate strategy include defining the organization’s mission, vision, and goals, identifying its core competencies, analyzing the competitive landscape, and making decisions about diversification, acquisitions, and resource allocation.
Q: What are the key elements of business unit strategy?
A: Key elements of business unit strategy include analyzing the competitive landscape, identifying target customers, developing product or service offerings, implementing marketing and sales strategies, and managing operational processes.
Q: How do corporate and business unit strategies work together?
A: Corporate strategy provides the overarching framework for business unit strategies, ensuring that all units are aligned with the organization’s overall goals. Business unit strategies, in turn, translate the corporate strategy into actionable plans and drive day-to-day operations.
Conclusion
Effective corporate and business unit strategies are essential for organizations to achieve sustainable growth and success in today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape. By understanding the distinction between these two strategic levels, organizations can effectively allocate resources, align initiatives, and achieve their desired outcomes.


