Entrepreneurship is creating, launching and scaling a new business venture. It involves identifying market opportunities, taking risks, innovating new products/services, mobilizing resources, and executing strategies to bring an idea to fruition.
Entrepreneurs have a vision, passion, and perseverance to turn ideas into sustainable, scalable enterprises that can disrupt industries and create value.
You probably heard the word entrepreneurship being thrown around often, usually around business conversations. These days, it might seem like everyone you meet claims to be an entrepreneur.
A clear definition of entrepreneurship helps us to know who’s genuine.
Before getting to that, knowing what it’s not is important. First, Entrepreneurship isn’t a young concept as it may seem. The word is French, dating back to the 18th century.

Entrepreneurship is not a loose term that anyone can adopt.
Certain parameters define an entrepreneur. It’s not a synonym for the unemployed. The business world is brutal, with no room for those with nothing to offer.
Then how do those “entrepreneurs” who don’t fit in a conventional niche or business field often do so well?
Table of Contents
What is the Definition of Entrepreneurship?
It’s building a new business from the ground up by introducing a new idea or concept. Most of the time, these businesses start small but always aim for expansion. These business ventures are risky because they are based solely on untried products or services.
The people who take these risks are called entrepreneurs.
People often confuse it with small businesses because they almost always start small. However, not all small businesses necessarily introduce new products or are ambitious enough to qualify as entrepreneurs.

A famous economist, Joseph Schumpeter, once defined entrepreneurship as “creative destruction.”
Creative because they gave birth to new concepts and ideas. Destructive because they rendered old industries outdated and, therefore, destroyed them. This constantly refreshes the market and is an adaptive tool for every economy.
The Role of Entrepreneurship in the Economy
Entrepreneurs now play a vital role in every national economy. This wasn’t always the case, however. Until recently, they were thought to offer very little to the economy as they mostly started small.
It wasn’t until the Austrian school of economics recognized entrepreneurship as the driving force of every economy in the 1800s. This is simply because a society’s progress is measured by how much it allows and encourages new ventures and ideas.
The fact is, products go out of date. This leaves an ever-expanding gap between supply and demand. The only way to fill this gap is through entrepreneurship and creating new products.

What Do Entrepreneurs Do?
Simply coming up with a new approach or idea for a product doesn’t fulfil the definition of an entrepreneur. Instead, entrepreneurship requires a wide range of skills, qualities and attitudes.
Certain responsibilities define entrepreneurship. These include:
- Making business plans: This includes a complete mapping of product development, sales and profit-making steps.
- Financing: An entrepreneur has to find ways to provide the funds needed to start working towards their goal.
- Hiring personnel: Matching the right people with the right job is difficult, especially in an emerging company.
- Leadership: Entrepreneurs must inspire employees to believe in the company’s vision and work towards united business goals.
- Risk aversion means finding the path towards business goals with the least risks and highest rewards.
- Complete responsibility for success and failure: At the end of the day, the very definition of entrepreneurship is venturing into untested territories. This entails a huge margin of failure for which the entrepreneur takes full responsibility and huge profit potential.
What is the Entrepreneurship Ecosystem?
A society’s progress is measured by how well it copes with economic peaks and troughs. This can be done by opening up new markets and businesses through innovative ideas. However, this doesn’t just happen by itself.
Instead, the right structures need to be in place to facilitate innovation.
An entrepreneurial ecosystem is a social and economic environment that surrounds local entrepreneurs and allows them to flourish. Many external factors directly affect any business and its profitability—for instance, economic downturns or shocks.
New businesses are especially vulnerable to these factors.
These factors are controlled mainly by surrounding businesses and monitored by governments.
A productive society should encourage people to become entrepreneurs by minimising the costs and risks involved. This often means offering space and resources to new entrepreneurs with promising ideas.
It should also support and inspire new ideas and accommodate out-of-the-box solutions.
Business Incubators
Business incubators provide guidance, support, and sometimes training to entrepreneurs. Incubators are a workspace for entrepreneurs to develop their ideas.
Typically, this involves a physical workspace of some description.
Creativity is boosted when like-minded individuals surround you because of the risky definition of entrepreneurship that can be off-putting if you’re on your own.
Business incubators are mainly focused on small startups. Being private companies, however, means they are selective with whom they provide their services.
Also, by agreeing to be part of an incubator, you often agree for the business incubator to take a stake in your startup, like a certain percentage or share.
Some services include training, motivation, workspace, proprietary protection, and sometimes even living accommodation.
Financing
A good idea is only as good as its execution. To make your vision a reality, you will need cash flow. One of the most important responsibilities of an entrepreneur is securing finance.
Because of the very definition of entrepreneurship, most startups don’t have the necessary funds at first; an entrepreneur sometimes needs to find external investors.
Pitching an idea to an investor is more than just inspiring them, it requires a full business plan because, in the end, business is about profit. Entrepreneurs may also seek external support for specialized needs such as M&A support to expand their ventures strategically. There are many ways to provide funds for an emerging business.
Venture Capital Financing
Venture capital is a type of financing involving a private equity firm. Entrepreneurs usually pitch their ideas to many private equity firms that, in turn, make offers to support the business in exchange for a share in the company. Using an investment teaser to kickstart your negotiations with investors and buyers is a working method to stand out among other startups.
The chosen firm provides financial support to get your company on its feet with the agreed-upon sum. The venture capital company releases the funds to the startup in stages like milestones.
These stages can be renegotiated at any time if there are problems, setbacks or other changes in circumstances.
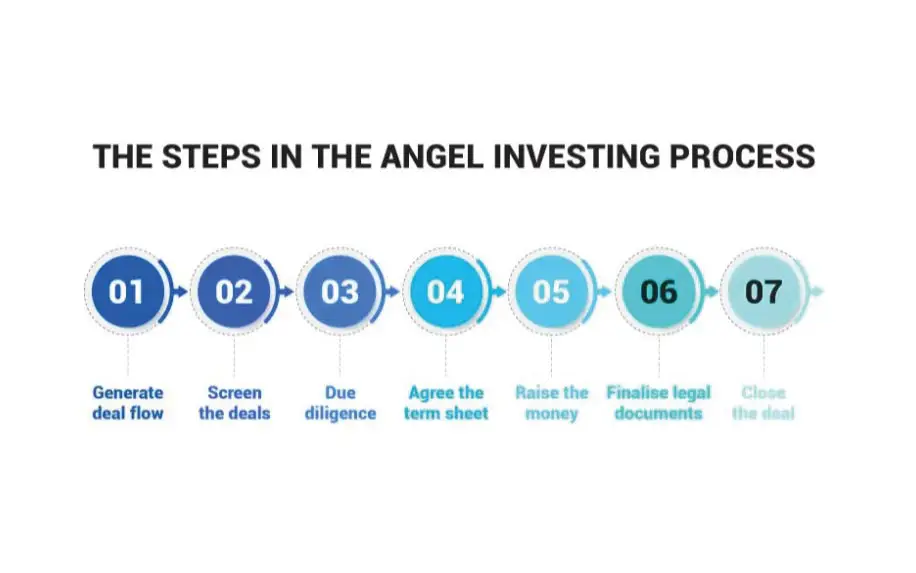
Angel Investors
This individual offers capital for a business in exchange for a returnable debt with interest or ownership equity. They invest in potentially profitable businesses that need immediate cash flow.
Nowadays, many angel investors provide their services online through crowd-sourcing websites.
Key characteristics of entrepreneurship:
- Opportunity recognition – spotting unmet needs in the marketplace
- Risk tolerance – willingness to take calculated risks
- Innovative problem-solving – developing new solutions
- Resource mobilization – accessing financial, social and human capital
- Adaptability – pivoting based on market feedback
- Value creation – building models that benefit customers and society
Comparing entrepreneurs vs small business owners:
While entrepreneurship results in starting new businesses, not all small business owners have an entrepreneurial mindset. Key differences include:
- Growth orientation – entrepreneurs aim for aggressive growth vs lifestyle stability.
- Innovation – entrepreneurs bring new ideas, small biz owners provide established goods/services
- Risk appetite – entrepreneurs are comfortable with uncertainty, and small biz owners avoid risk.
- Funding – entrepreneurs raise investments to scale, small biz may bootstrap or avoid loans
Opportunity Recognition:
Entrepreneurs have a keen eye for identifying unmet needs in the marketplace and developing innovative ways to solve problems. They spot gaps in products, services, and experiences that present opportunities.
Some examples include:
- Recognizing consumers’ desire for more convenience and developing an on-demand delivery model
- Identifying sustainability as an emerging value and creating products that align with it
- Realizing small businesses need more accessible tools and building simplified software platforms.
Effective entrepreneurs continuously analyze trends, shifts in consumer behaviour and market inefficiencies. They brainstorm fresh ideas and say “what if” to imagine better solutions.
Risk Tolerance:
Entrepreneurs have a higher appetite for risk and can handle uncertainty. While calculated risks are taken, they use various techniques to de-risk new ventures:
- Validating demand before going to market
- Starting lean and iterating based on customer feedback
- Partnering with experts to fill knowledge gaps
- Building in testing phases before full rollout
- Creating contingency plans and emergency reserves
Being comfortable with uncertainty allows entrepreneurs to make bold moves when opportunity strikes. They accept that failures may happen but focus on learning.
Entrepreneurship: Why Take the Risk?
Almost everyone indeed wants success and wealth, but when it comes down to it, not everyone would risk it all for an idea. Ideas alone won’t pay the bills. Entrepreneurship requires hard work.
For many people, this is simply overwhelming. For others, the reward is motivation to carry on. Entrepreneurs have the freedom and flexibility to be their boss and carve their path in life.
Additionally, entrepreneurs are the backbone of every economy. The definition of entrepreneurship makes them visionaries, ambitious leaders who guide the business world to the future.
New ideas aren’t for the sake of new ideas, but they provide an actual service and make life easier if only a little bit. Why take the risk? Because it’s worth it. Because if you believe in your idea enough and do your research, the profit outweighs the risk every time.
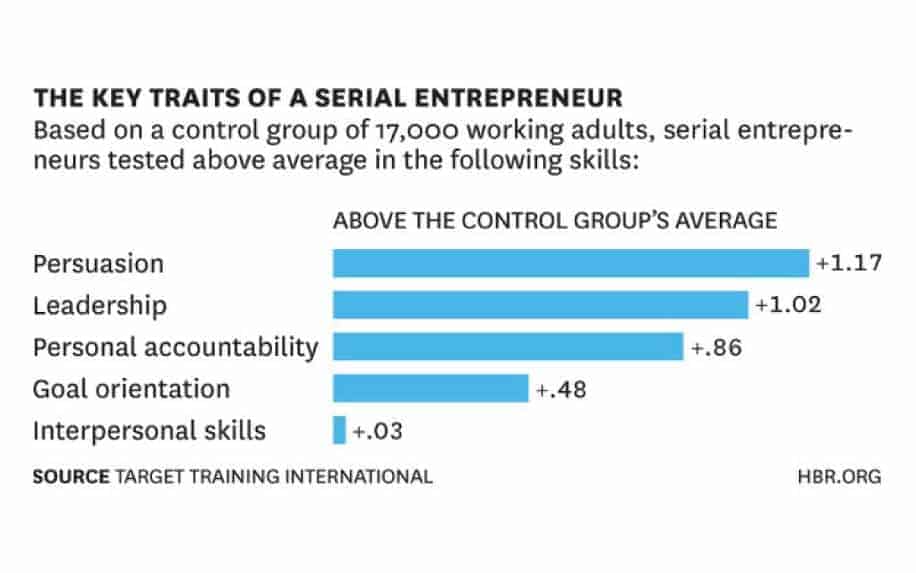
Entrepreneurial Mindset:
Successful entrepreneurs share common traits and attitudes.
Key elements of an entrepreneurial mindset include:
- Passion – Entrepreneurs have intense enthusiasm for their ideas and drive to turn them into reality. They deeply believe in their vision.
- Perseverance – The ability to push through challenges, failures, and obstacles is critical. Entrepreneurs don’t give up easily when faced with adversity.
- Vision – Keeping the big picture vision in mind guides all decisions and motivates action. Seeing future possibilities is key.
- Leadership – Influence, delegation, motivation and team-building are needed to execute ideas. Entrepreneurs lead by example.
- Creative Problem Solving – Unconventional thinking and ingenuity lead to innovative solutions. Entrepreneurs find ways over, around or through barriers.
- Continuous Learning – Rapid iteration, prototyping, and market testing enable adapting. Intellectual curiosity is important.
Entrepreneurship Ecosystem:
Succeeding as an entrepreneur often depends on the ecosystem of support in place.
Key elements include:
- Networking with other entrepreneurs to share lessons learned, get advice and find synergies.
- Find mentors experienced in your industry who can provide invaluable guidance to avoid pitfalls.
- Building a strong team with complementary skillsets and an entrepreneurial spirit.
- Taking advantage of local startup accelerators, incubators, meetup groups and training programs.
- Engaging early adopters and influencers who can test products and promote your launch.
- Participating in pitch competitions to hone your narrative, get exposure and meet investors.
Entrepreneurial Marketing:
Promoting and selling as a startup requires creative, cost-effective marketing tactics.
Common techniques include:
- Guerilla marketing uses non-traditional, theatrical tactics to generate buzz.
- PR outreach, guest posting and media publicity to build credibility and reach.
- Social media engagement with visual content, micro-influencers and hashtags.
- Content marketing through blogging, videos, and case studies to attract and retain customers.
- Releasing a minimal viable product to test and get real user feedback quickly.
- Referral marketing offers existing customers incentives to share your brand.
Entrepreneurship FAQ
Q: Does entrepreneurship require special education or training?
A: There are no specific education requirements. Real-world business experience, mentorships and online courses can provide knowledge.
Q: What percentage of startups succeed long-term?
A: According to Small Business Administration data, about 20-25% of startups survive beyond their first 5 years.
Q: What are the most important entrepreneurial skills?
A: Key skills include risk tolerance, perseverance, resourcefulness, vision, passion, leadership and creative problem solving.
Q: Is entrepreneurship mostly nature or nurture?
A: There are examples of natural entrepreneurs and those who cultivated skills over time. But some innate tendencies do help.
Entrepreneurship Conclusion:
Entrepreneurship is about having the vision, mindset and skills to solve problems and fill market needs through new ventures. Entrepreneurs invent innovative solutions and push progress forward by continuously scanning their environment, asking ‘what if’, and spotting opportunities.
Yet bringing ideas to life demands grit, calculated risk-taking, mobilizing resources and leading motivated teams. Entrepreneurial success also relies on cultivating networks and ecosystems for advice and support.
While challenging, entrepreneurship can provide immense personal and social rewards when done thoughtfully and passionately. This guide has covered the key elements, characteristics and processes defining modern entrepreneurship.


