No matter what your position is in the business world, the first thing you learn is the importance of understanding your customers. The various types of customer segmentation are crucial here.
Even if you’re a customer, it’s almost always better to find someone who specialises in what you need. The closer a business’ offering matches a customer’s needs, the better.
So what is customer segmentation? In the end, all businesses want to gain the trust of their customers. Having a clear picture of the different people who benefit from your products and services is a huge part of this.
Table of Contents
What Is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation, also known as market segmentation, is the practice of dividing consumers into subgroups. This makes it easier to target your messaging more closely to your customers’ needs.
To further refine your marketing strategies, consider leveraging big data analytics services. These services can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends, enabling you to make data-driven decisions that enhance your overall marketing effectiveness.
All sorts of data can inform your market segmentation. For example:
- Social factors,
- Economic factors,
- Demographics,
- Product uses,
- Behavioural preferences.
Segmenting your market according to customers is a sound practice. It empowers you to build up a more solid understanding of your clients and find what influences them. When you’re conveying a message, it will be more compelling if it resonates with customers. The division is essentially a method for orchestrating your clients into smaller gatherings as indicated by write. Each segment should be described by specific traits.
Customer Segmentation Meaning
Customer segmentation refers to dividing customers into groups that share similar characteristics, needs, interests, or behaviours. It is a key strategic marketing concept that allows companies to better understand their customers and tailor products, services, and messaging to resonate more effectively with different segments.
Some key things to know about customer segmentation:
- It groups customers based on common factors like demographics, geography, psychographics, buying preferences, etc.
- Key segments are identified through market research and data analysis.
- It allows personalized marketing rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
- Companies can develop targeted products, offers, and communications for each segment.
- It helps determine better product positioning and pricing strategies.
- Common bases for segmentation include age, gender, location, income level, lifestyle, values, usage rate, etc.
- Benefits include improved customer satisfaction, increased conversions, and higher profitability.
- Examples could include segments like “budget-conscious moms”, “affluent retirees”, “fitness enthusiasts” etc.
Customer segmentation is a crucial process that allows organisations to divide customers into distinct groups with common needs and behaviours so marketing can be tailored for greater relevance, engagement and impact with each segment.
4 Types of Customer Segmentation
Market segmentation is important when attempting to sell any kind of product, but it’s important to choose the right strategy.
There are a number of different types of customer segmentation. Some of these include:
- Geographic segmentation,
- Demographic segmentation,
- Psychographic segmentation,
- Behavioural segmentation.
1. Geographic
Geographic segmentation is the act of dividing your market in light of where they are found. Sections can be as wide as a nation or a district, or as thin as one road of homes in a town. in other words, it divides customers into regions, countries, states, cities, and neighbourhoods, which is useful for localisation strategies.
Furthermore, geographic division is valuable for all kinds of companies. Large organisations with global markets may offer items to people in different areas. For instance, you might specialise in selling skis and winter equipment. Introducing this promotion to hot regions, for example, would be pointless, and could even desensitise the public to future commercials.
Especially for independent companies, geographic division can be utilised to target particular clients without wasting resources on impressions that won’t transform into deals. For instance, a neighbourhood cafe could exhibit its advertisement to just individuals inside the town they are located.
Geographic customer segmentation is one strategy that is easy to implement.
2. Demographic
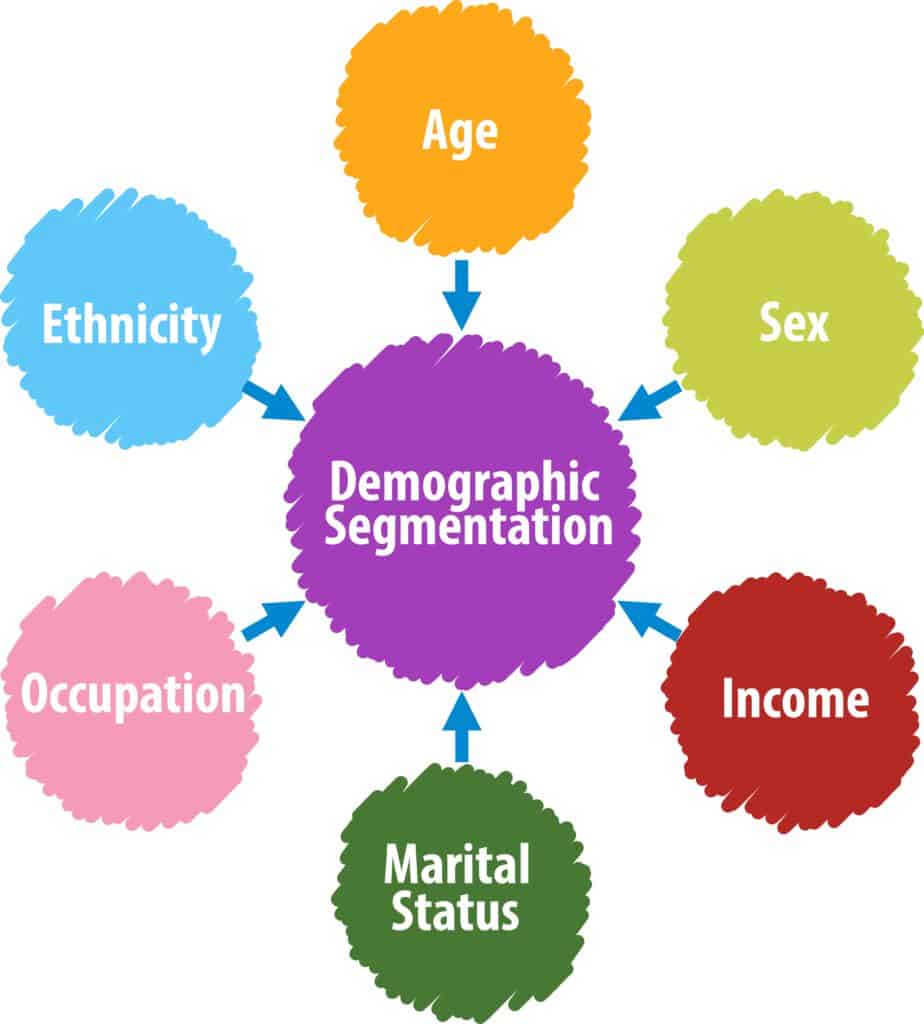
The demographic division is sectioning the market in view of specific attributes of the gathering of people. Qualities frequently include:
- Age,
- Sex,
- Religion,
- Salary,
- Occupation.
Additionally, genuinely simple to execute, demographic division can be helpful in countless ways. Luxury brands may market to a demographic who earns more than £100,000.
Universities may mainly market to 17-22 year olds.
Demographic segmentation is much more effective while focusing on different segments at the same time. Imagine you ran an email campaign focused on neighbourhood females, 25-50 years of age, with a family unit wage of under £50,000.
Basically, this means you employed multiple demographic criteria such as age, sex, and income. Joining many customer segmentation criteria can possibly achieve an exceptionally greater outcome.
3. Psychographic
Psychographic customer segmentation is far less concrete than both geographic and statistical client division, as the qualities used to section are less “substantial” than the last two.
Psychographics divides the market based on factors such as way of life, values, socioeconomic class, and identity.
This kind of client division is essentially more hard to execute than geographic or statistical division.
To appropriately portion the market in light of psychographics, advertisers should truly set aside the opportunity to become more acquainted with their present and past clients.
This means identifying the perfect purchaser persona for the item or administration and creating relationships with the client base.
A prime case of psychographic division is focusing on the individuals who are thrifty. These individuals esteem a decent arrangement and have a tendency to be brilliant customers.
Retail stores use this strategy more than anyone. Utilising marketing messages like “Amazing Prices” and “Best Online Specials” since it will resonate with the consumers they are trying to reach.
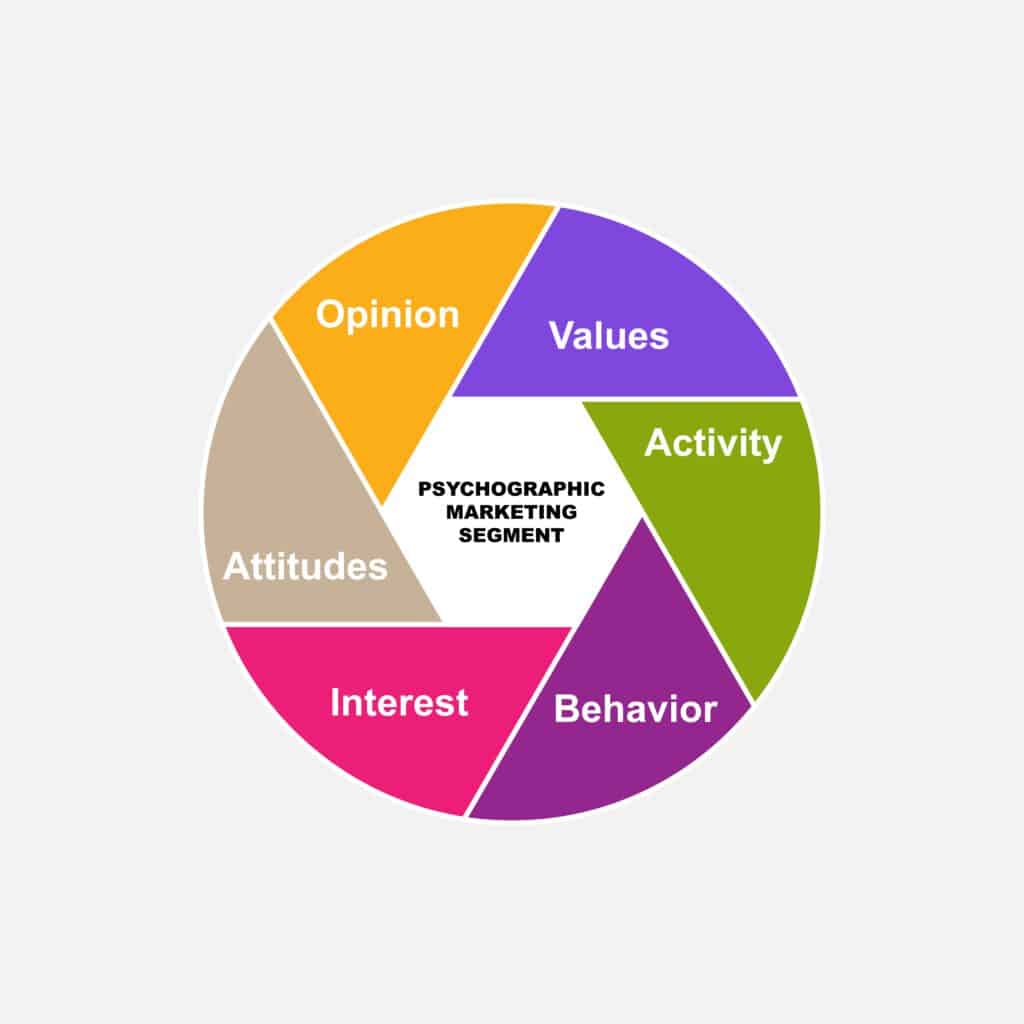
The 5 Factors of Psychographic Segmentation
Lifestyle
Lifestyle centres around how a consumer lives their life. It asks questions like whether are they married, have children, and what’s their daily routine. Consumers that live a healthy lifestyle would be attracted to fitness and well-being products and services. For example, a business that sells vegan foods would target healthy lifestyle consumers as opposed to consumers who heavily drink and smoke.
Social Status
Social status considers where a consumer is placed in society and what social class they belong to. Take an expensive jewellery brand for example, they will target the upper class as they know they will buy luxury items whereas the middle class are more likely to look for affordable products at the best value.
Attitudes
A consumer’s attitude and personality have a great impact on their buying decisions. Attitudes are formed by one’s social class and cultural background. People will have different attitudes based on how they were brought up. Continuing with the social status example, a consumer who grew up in the upper class may prefer going to expensive restaurants instead of fast food diners as this is what they are accustomed to.
Activities and Interests
Activities and Interests are closely linked to a consumer’s buying habits. Someone who is very adventurous will spend their money on hiking boots if they like to go hiking similarly, someone who has an interest in fashion might invest their money in vintage pieces of clothing. We all have different hobbies we are interested in and they can directly impact how we purchase.
Opinions
Learning what your consumers think about your product or service is important in understanding what they want and need. For example, a consumer might be of the opinion that businesses should use more eco friendly packaging for their products therefore, they won’t buy from businesses who use a lot of plastic in their packaging as this would be against their views.
4. Behavioural
Behavioural segmentation is the act of isolating buyers into groups as per any of the accompanying characteristics:
- Utilisation,
- Loyalties,
- Mindfulness,
- Events,
- Learning,
- Purchase intents.
Behavioural customer segmentation can be utilized as a part of an assortment of ways.
Behavioural division enables advertisers to be more applicable and create information that will resonate well with their target audience. We see behavioural segmentation used a lot by streaming services. They use algorithms to track consumer behaviours while on the service in order to customise the content they show to them. Every time you watch, rate or skip a movie or show, it gives the streaming service more information on your behaviour and allows them to make recommendations for you.
Unlike Demographic and Geographic Segmentation, Behavioural and Psychographic segmentation get to know the consumer themselves and can tell a lot about them, rather than seeing a customer in every individual they can see the individual in every customer.
Why Is Customer Segmentation Important?

Creating a corporate strategy without first employing an effective customer segmentation strategy would be a shot in the dark. You’re unlikely to have much success if you don’t know who you’re targeting.
There are many benefits of customer segmentation, one being it helps you to spend money efficiently. This is because segmentation helps you to decide which marketing strategies deserve different allocations of resources.
Furthermore, a lack of an effective customer segmentation plan can cause uncertain product development strategies. Together, all of those variables can slow or stop a company’s progression.
When customer segmentation is done well, the business benefits are huge. For instance, a customer segmentation strategy can unmistakably affect your working outcomes in the following ways.
Improving Your Product
Customer segmentation helps you to improve your product, through a better understanding of who uses it. Ultimately, this will lead to more sales. The advantages likewise stretch out past your core product offering.
Any bits of insight into your best clients will enable you to offer better customer care, administration, and whatever other offerings that make up their experience with your brand.
Focusing Your Promoting Messages
Along with product changes, customer segmentation can enable you to craft more engaging messages. Allowing each segment to receive customised messages brings about higher-quality enthusiasm for your brand and also allows for better communication between you and your target audience.
A huge benefit of customer segmentation is that it leads to customer retention. When customers are targeted with messages and products specified to them and are made to feel that their needs and wants are understood and met by the business, they are more likely to stay.
Seeking New Sales Opportunities
Segmentation allows you to focus resources on the channels and customers who provide the best return on investment. This way your business group will have the capacity to expand its win rate, make more progress, and better revenues.
Gain Competitive Advantage
Market Segmentation allows you to stay in front of the competition by providing personalised products and services to customers. The more accurate your customer segmentation the better you will be able to meet customers expectations and build brand loyalty.
Economies of Scale
When you know what market to target with your product and service you will no longer waste time and resources on markets that you will not be profitable in. Accurately allocating your assets across your markets with help you acquire economies of scale.
Other Types of Market Segmentation
Market Segmentation doesn’t just stop at the 4 main types we have looked at. There are many different varieties of segmenting that you can use to target your market. Let’s have a look at a few more.
Value-based Segmentation
Value Segmentation, also known as Transactional Segmentation, groups together customers who have similar spending patterns. Customer segmentation models are often used by businesses to target audiences.
Transactional Segmentation uses an RFM Modelling-Recency, Frequency, Monetary- to source the business’s most valuable customers.
Take an online clothing brand for example; if a customer spends on average £100 every time they shop online with them then the clothing brand will target this customer with their more expensive clothing.
Likewise, if a customer likes to save money and will only spend £40 when they shop online then the clothing brand may target them with discounts and offers to entice them onto their website.
Being able to analyse customer’s spending habits can lead to price optimisation as it allows you to price your products to match your target audience accurately.
Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic Segmentation looks at segmenting Business-to-Business (B2B) consumers. It can group its consumers by industry type, location or company size. Firmographics is used for other businesses the same way demographics is used for customers.
Needs-Based Segmentation
This type of segmenting looks at why customers need a specific product or service. It asks the question why does a customer want to purchase a certain item? Needs-based segmentation groups, consumers need from functional to emotional.
A functional need is a product or service needed by the consumer in order to perform a task. For example, a consumer may begin working from home therefore, they may need to buy a computer in order for them to do their job.
An emotional need refers to how a customer wants to feel by using your product or service. An emotional need would be a need for security. A consumer with this need may buy a security alarm or install a peephole in their door in order to satisfy their need to be safe and secure.
Usage Rate Segmentation
Usage rate segmenting focuses on how much the consumer uses a product or service. It allows you to see how much consumers are interacting with a product at a certain time. User segmentation works well with seasonal segmentation.
An example of this would be the demand for BBQs and parasols increasing during the summer as more consumers are using these products at this time of the year. A store will know this purchasing habit by looking at the past usage rate and will be prepared by having extra stock.
Applying Customer Segmentation Efficiently
Knowing the customer segment criteria is only half the equation. The next step is to fully integrate your own customer segments into your business. However, first, you need to gather data specific to your company with a customer segmentation strategy, this can be done by:
Identify the Target Market & Expectations
Identify the target market by finding a common interest, goal or value among the target audience and dividing your customers up based on these categories. Targeting the market aids in the planning and organization of marketing strategies based on the market size and preferences of the target audience.
It’s essential to figure out the target market’s needs and expectations in order for you to meet these requirements.
Set Marketing Segmentation Objectives
It’s important to set customer segmentation objectives to ensure you stay on track. The SMART framework is very useful to make sure you stay aligned with your objectives. An example of using the SMART framework for customer segmentation would be the following;
- Specific: A clothing business wants to increase the traffic of students on its website.
- Measurable: The goal is to increase the traffic from this target group by 10%.
- Achievable/Agreed: Traffic increased in this age group during Black Friday Sales, showing this target group prioritises value for money. Having a student discount will make this goal achievable.
- Relevant/Realistic: Increasing traffic on the website will create brand awareness and increase competitive advantage.
- Time-Bound: 3 months
Read more on how to set objectives and goals for your business.
Choosing Which Data is Relevant
Among all the many types of customer segmenting, you need to figure out which are most relevant to your business.
Furthermore, you need to figure out which criteria from each will offer the most insight on your targeted customer. For example, which age group and gender in demographics? Which spending patterns and shopping locations are in specific behaviour segments?
Gathering Information
After choosing which data to collect, you’ll need to find the best way to collect this data. The internet is your number one source for data collection on potential clients.
Facebook ads are a perfect way to research customer data. Google Analytics is another great tool for client data. Surveys can also be used to provide direct data from the clients. Read more about Google Analytics: Here!
The past numbers of the business itself, from all departments, are the best indicators for developing new segmentation methods.
Establishing a Line of Communication with All Departments
The purpose of a successful customer segmentation strategy is to enhance the overall performance of a business. This is why it’s critical to relay all customer investigations and findings to and from all the departments within a business.
The marketing department, for example, can give data on the outreach and interactions of an ad campaign, as well as, utilise information from the newest customer segmentation research in creating more effective campaigns.
Customer Segmentation Analysis
Conducting customer segmentation analysis is relatively simple if you know what you’re doing. Check out these steps to help guide you through the process.
- Identify Your Goal
First, clarify what you hope to achieve through customer profiling and segmenting. Do you want to improve targeting? Craft personalised messaging? or identify new opportunities? Understanding your objectives will help inform how you conduct your analysis.
- Gather Data
Collect relevant customer data from your CRM systems, web analytics, social media insights, surveys, and other sources. Demographic, behavioural, psychographic, purchase history, and channel use data will prove valuable. Make sure your data is accurate and recent.
- Identify Key Segmentation Criteria
Review your data to determine what parameters would make sense as segment criteria. Common factors include demographics, location, purchase behaviour, channel usage, motivations, etc. Choose criteria that relate best to your goals.
- Perform Statistical Analysis
Use data mining techniques and statistical analysis methods like cluster analysis to group customers based on common characteristics. Tools like R and Python can help analyze large datasets.
- Develop Customer Profiles
Analyse and document key attributes of each resulting customer segment. Create detailed profiles highlighting demographics, behaviours, motivations, interests, and segment size.
- Evaluate and Refine the Segments
Assess the quality of your current solution. Look for identifiable, substantial, accessible, stable, and useful segments. Don’t be afraid to refine if needed to arrive at distinct groups.
- Apply Insights
Use the segmentation insights to guide marketing, products, and communication strategies tailored to your high-value customer groups. Continually refine through testing and measurement.
Leverage Different Types of Customer Segmentation
The difference between an average business and a leader in the industry is that a leader never stops growing. The truth is there is no one magic recipe for finding the best customer segmentation for life.
What the customer wants or needs is an ever-changing game and the key is to always be ahead. The only way to do that is to mix and match all segmentation types in order to find the perfect customer.
However, it doesn’t stop at that, you need to keep researching and perfecting your image of the target client forever. Investing time and money in your customer profiling will provide the best results.
Customer Segmentation Template
In order to help you segment audiences more clearly, check out this template below. You can customise it further depending on your target group.
Segment Name / Description: Briefly summarise key attributes of this segment.
Key Demographic Attributes
- Age range:
- Gender:
- Location/Geography:
- Income level:
- Education level:
- Occupation/Profession:
- Other:
Psychographic Profile
- Values/Attitudes:
- Interests:
- Lifestyle:
- Motivations:
- Challenges/Pain Points:
- Other:
Behavioural Attributes
- Product/Service usage rate:
- Purchasing habits:
- Channel preferences:
- Brand preferences/loyalty:
- Price sensitivity:
- Buying stage:
- Other:
Fill out a template like this for each key customer segment identified through your analysis. Tailor the attributes and strategies based on your business and update as you gather more data on each segment over time.
Customer Segmentation Using Machine Learning
Customer segmentation using machine learning is a powerful approach to categorising customers into distinct groups based on their behaviours, preferences, or characteristics.
Traditional customer segmentation is often based on demographic data such as age, gender, and income. While this approach can be effective, it doesn’t always capture the nuances of customer behaviour or preferences. Machine learning, on the other hand:
- Can handle large datasets and uncover patterns that might be missed by human analysts.
- Can segment customers based on a combination of features, including purchasing behavior, browsing history, and more.
- Continuously learns and adapts to new data, ensuring that customer segments remain relevant over time.
- Natural language processing can analyse customer surveys, reviews, and social media to identify sentiments, interests, and behavioural patterns for segmentation.
- Anomaly detection flags outlier customers that don’t fit segmentation models. This helps identify opportunities or issues.
- Unsupervised learning algorithms like cluster analysis can identify groups of similar customers in data. Algorithms group customers based on behaviours, attributes, demographics etc.
- Supervised learning models can classify customers into predefined segments using training data. For example, predictive modelling can determine key attributes of high-value customers.
The main benefits of using machine learning include finding segments in complex data, continual refinement of models, and automation of analysis for optimal results. Segmenting customers using machine learning offers a data-driven way to understand and cater to the diverse needs of customers. By leveraging the power of machine learning, businesses can make more informed decisions and enhance customer satisfaction.
Customer Segmentation Analysis with AI
Customer segmentation with Artificial Intelligence has become increasingly popular due to its ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns that might be difficult for humans to discern. Here are some user-friendly ways to achieve this using AI:
- Clustering Algorithms:
- K-Means Clustering: This is one of the most popular methods. It divides customers into a predetermined number of clusters based on their attributes.
- Hierarchical Clustering: This method creates a tree of clusters. It’s useful if you want to understand hierarchical relationships between clusters.
- DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise): This method creates clusters based on the density of data points.
- Decision Trees:
- These are simple, visual tools that can help sort customers based on specific criteria. They can be easily interpreted and are often used in conjunction with other methods.
- Neural Networks:
- Self-Organizing Maps (SOMs): These are a type of neural network that can be used for feature detection. They’re particularly useful for visualizing high-dimensional data.
- Autoencoders: These neural networks can reduce the dimensionality of data, making it easier to segment.
- RFM Analysis with AI:
- RFM stands for Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value. Traditional RFM analysis segments customers based on these three attributes. By incorporating AI, you can fine-tune this segmentation to be more accurate and reflective of subtle patterns in the data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- If you have textual data from customers (like reviews or feedback), NLP can be used to segment customers based on sentiment, topics of discussion, or other textual patterns.
- Predictive Analytics:
- Using historical data, AI can predict the future behaviours of customers. This can be used to segment customers into groups like “likely to churn” or “likely to purchase.”
- Recommendation Systems:
- While traditionally used to recommend products, these systems can also be used to segment customers based on their preferences and buying habits.
- Visualization Tools:
- Tools like t-SNE (t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding) can be used to visualize high-dimensional data in two or three dimensions. This can help in visually identifying clusters or segments.
- User-Friendly Software and Platforms:
- There are many platforms that offer AI-powered customer segmentation as a service. These platforms often come with intuitive dashboards and visualization tools. Examples include IBM Watson, Salesforce Einstein, and Adobe Analytics.
- Ensemble Methods:
Combining multiple AI models can often lead to more accurate segmenting. For instance, you might combine the results of a clustering algorithm with a decision tree to get a more nuanced understanding of your customer segments.
When implementing any of these methods, it’s crucial to:
- Understand the business context and objectives.
- Regularly validate and update the segmentation model as customer behaviours and market conditions change.
- Ensure that the data being used is clean, relevant, and unbiased.
Lastly, while AI can provide powerful insights, it’s essential to combine these insights with domain knowledge and human intuition for the most effective customer sorting.
Customer Segmentation Python
Python is a widely used high-level programming language, using this to segment your audience is a bit more advanced if you’re not used to working data analysis software. It is an interpreted, object-oriented, open-source language with a clear and readable syntax. It is designed to be simple, easy to learn and highly readable, and can be used for a wide range of purposes, including customer segmenting.
Here are some ways to approach customer segmentation using Python:
Import libraries: Import NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn, Matplotlib, Seaborn etc. for data operations and modeling.
Load dataset: Import customer dataset CSV into a Pandas DataFrame. Check for data quality issues.
Data preprocessing: Handle missing values. Encode categorical features. Standardize data.
Feature engineering: Derive new features like customer lifetime value, frequency of purchases etc. that aid segmentation.
Apply algorithms: Use Scikit-Learn libraries like KMeans clustering or decision tree classifiers to segment data.
Model evaluation: Evaluate segmentation quality by metrics like silhouette score. Visualize clusters using Matplotlib.
Profile segments: Analyze and document key attributes of each segment – demographics, behaviours etc.
Optimization: Fine-tune model hyperparameters like the number of clusters using techniques like grid search.
Prediction: Develop a model to predict customer segment membership for new data points.
Key Python libraries used include Pandas, Scikit-learn, NumPy, Matplotlib, and Seaborn. The workflow involves exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, application of ML algorithms, and profiling of customer segments. The output provides actionable insights for tailored marketing results.
Customer segmentation dataset
If you plan on getting down to the nitty-gritty details of market sorting using raw data, you first need to access the datasets – but where can you get them? There are several publicly available datasets that you can use to practice or implement market segmentation techniques. Here are some popular dataset sources:
- UCI Machine Learning Repository:
- The UCI repository is a collection of databases, domain theories, and datasets that are used by the machine learning community. There are several datasets related to market segmentation, such as the “Online Retail” dataset, which contains transactions occurring between 01/12/2010 and 09/12/2011 for a UK-based online retail.
- Kaggle:
- Kaggle is a platform for predictive modelling and analytics competitions. It has a vast collection of datasets uploaded by its community. Some popular market sorting datasets on Kaggle include:
- Mall Customer Segmentation Data
- E-commerce Data
- Credit Card Dataset for Clustering
- Kaggle is a platform for predictive modelling and analytics competitions. It has a vast collection of datasets uploaded by its community. Some popular market sorting datasets on Kaggle include:
- Data.gov:
- This is the U.S. government’s open data site, and while it might not have datasets explicitly labelled for market segmentation, there are many datasets related to consumer behaviour, finance, and other areas that could be repurposed for segmentation exercises.
- Datasets for Specific Domains:
- Depending on the industry or domain you’re interested in, there might be specific datasets available. For instance:
- For telecom: The “Telco Customer Churn” dataset.
- For finance: Datasets related to credit card usage or bank transactions.
- For retail: Purchase history datasets.
- Depending on the industry or domain you’re interested in, there might be specific datasets available. For instance:
- Synthetic Datasets:
- If you’re just looking to practice or demonstrate a technique, you might consider using tools to generate synthetic data. This way, you can create a dataset tailored to your needs without any privacy concerns.
If you plan on using datasets frequently, it may be worth purchasing a membership for one of the above platforms, however, you can usually access good datasets for free on Kaggle.
How often should market segmentation be done?
There is no set rule on how often market segmentation should be done. However, here are some general guidelines for reviewing and revising your strategy:
Annually
An annual re-evaluation of market segments is common, especially if entering a new fiscal year or aligning with annual planning cycles. Look for significant shifts over the past year.
Quarterly
More frequent quarterly reviews allow you to spot emerging trends and changes in the market. Adjusting and pivoting if needed.
Major events
Evaluate after events like product launches, acquisitions, expansions into new markets, new competitive entries, or macroeconomic shifts.
Customer or market changes
If you notice changes in customer behaviours, new customer attributes, new data availability, or new market opportunities, re-assess segments outside the normal cycle.
Campaign launches
Examine the effectiveness of existing segments prior to major campaign launches or marketing spending decisions.
The optimal frequency depends on the industry, business model, and market dynamics. But annual or quarterly reviews are common. The goal is to balance the effort required versus keeping segments aligned with the market. Monitor for changes warranting re-segmentation, and don’t hesitate to reevaluate if segments grow stale.
SEE MORE: AI in Marketing | Free GA4 Training | What is SQL?


