Future planning and strategic organisation are critical for business success, and a lack of them is often the leading cause of business failure. Business objectives and goals give your business something to work towards, a vision to achieve and ultimately – a purpose for going to work every day!
Whether it’s a new project, a marketing strategy, or an annual strategic plan, business objectives are always invited to the party. This article introduces business objectives and goals, why they matter and how you can achieve them for success.
Table of Contents
Definition of Business Objectives
“A business objective is a detailed picture of a step you plan to take to achieve a stated aim.”
Business objectives are a company’s specific, measurable, and time-bound goals to achieve its broader mission and vision. They provide a clear direction for the organisation, serve as a benchmark for performance, and guide strategic decision-making.
Business objectives are typically set across different levels of an organization and can encompass areas such as sales, profitability, growth, market share, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and innovation, among others. They are essential for aligning the efforts of various departments and ensuring that the company remains focused on achieving its overarching aims.

Difference between business goals and business objectives
Objectives and goals may be used interchangeably. However, they are not the same. Goals are the headlines, the final destination you want your business to reach, whereas objectives define your journey’s what and how details.
Think of it this way: the goal is to go on holiday from Ireland to Portugal. The objectives include specific details like which transportation you will take, how long the journey will last, how much the ticket costs, etc. Both concepts are important and intrinsic to business success.
In addition to the above point, business objectives and goals employ two languages. Goals usually use emotional and creative language since they express dreams or final achievements. Meanwhile, objectives usually speak in terms of numbers, percentages, and deadlines, practical language.
Why do you need to set business objectives?
Setting business objectives will help you define a road map for your business’ growth and performance. Without knowing where you are going, you will have no direction and eventually get lost. In terms of business performance, this could mean losing profits, wasting resources and not seizing the opportunities when they pass by.
Your goals are the source for any new ideas you want to introduce to your business. Take this, for example your business wants to be more involved in the local community, so you might consider pursuing business objectives such as sponsoring a local sports team or taking part in a charity run.
Goals help your business have a focus. In the meantime, objectives give your goal a means for obtaining it.
Why are business objectives important?
Business objectives are a company’s specific, measurable goals to achieve its broader mission and vision in a given period. They provide direction, motivate employees, and offer a foundation for measuring performance and making strategic decisions.
- Direction: They provide a clear path for the company, ensuring everyone is aligned and moving towards common goals.
- Motivation: Clear objectives can inspire and motivate employees by giving them a sense of purpose and achievement.
- Performance Measurement: Objectives offer benchmarks against which the company’s performance can be measured, allowing for adjustments and improvements.
- Resource Allocation: By setting priorities, objectives guide where resources (time, money, personnel) should be allocated.
- Risk Management: Clear objectives can help identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Business objectives are essential for guiding a company’s actions, evaluating its performance, and ensuring long-term success. They should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the evolving nature of the business environment and the company’s growth and development.
Types of Business Goals
Your business objectives may vary depending on the nature of your business, the industry, the competition, etc. Below are some common types of business objectives. Consider them all and determine which would best meet your business’ vision.
- Profitability Objectives: Goals related to achieving a specific profit margin, return on investment (ROI), or overall profit figure.
- Growth Objectives: Aim for expansion, such as increasing sales by a certain percentage, expanding to new markets, or launching new products or services.
- Market Share Objectives: Goals to capture a specific percentage of the market or to increase the company’s market share by a certain amount.
- Operational Efficiency Objectives: Focused on improving internal processes, reducing costs, or increasing production efficiency.
- Customer-Related Objectives: Goals related to customer acquisition, retention, satisfaction, or loyalty. Examples include reducing customer churn rates or achieving a specific Net Promoter Score (NPS).
- Innovation Objectives: Aim to develop and launch new products, services, or technologies.
- Employee-Related Objectives: Goals related to employee satisfaction, retention, development, or recruitment.
- Social and Environmental Objectives: Goals related to corporate social responsibility (CSR), such as reducing the company’s carbon footprint, engaging in community service, or achieving specific sustainability targets.
Setting business goals that are meaningful to your business is also important. Ask yourself where you see this business in five years and what you will do to get there – these questions will help you identify what business goals you should pursue.
Who should you communicate your business objectives to?
Communicating your business goals and objectives is essential to securing their success. You should communicate them to key stakeholders, employees and customers – check out the reasons below.
Stakeholders
Communicating your strategic vision with key stakeholders is essential to garner support for your business. Stakeholders might include potential/current investors or shareholders, so they must trust your judgment in setting business goals and objectives.
Employees
Understanding the objectives and goals of the company motivates your employees and makes them feel that they are a part of the mission. Communicate your business goals from the top down and ensure that key information is passed on. Your employees are one of your greatest assets in achieving business objectives, so they need to know what they are doing and the reason why they are doing it.
Customers
You would be surprised how quickly your customers/clients can become your biggest supporters of your business goals. Ensure that you communicate your strategic vision with those who support your business; it will help set you apart from the competition and encourage your audience to become enthusiasts of your business.
SMART Objectives
SMART objectives enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of goal-setting and execution. They provide a structured approach that increases the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes, making them a valuable tool for businesses in achieving their goals and objectives.
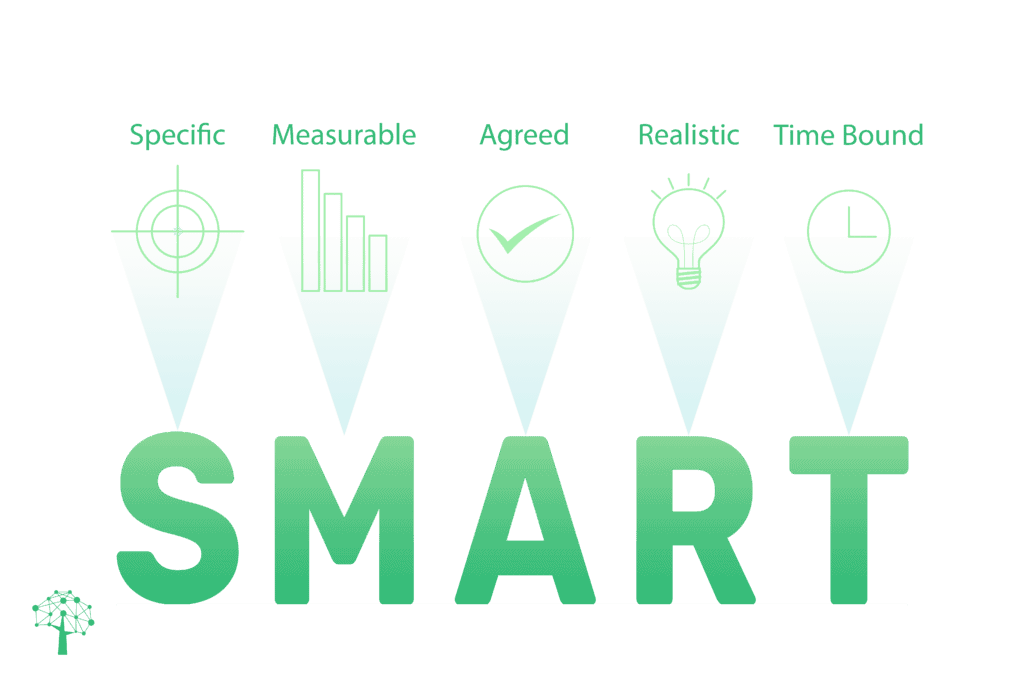
SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a framework to set clear and well-defined objectives – helping you identify exactly what you need to do to get the desired results.
Specific
The objective should be clear and specific, answering questions like: What do I want to accomplish? Why is it important? Who is involved?
Measurable
It’s essential to track the progress and measure the outcome. Questions to consider include: How much? How many? How will I know when it is accomplished?
Achievable
The objective should be realistic, given the available resources and time. It should stretch your abilities but still remain possible.
Relevant
The objective should align with broader goals and be worthwhile. It should answer the question: Does this seem worthwhile? Is this the right time?
Time-bound
Setting a target date for deliverables is crucial. It answers the question: When will this be accomplished?
Why Do SMART Objectives Matter?
SMART objectives help you in making a real commitment to achieving your business goals. Check out why they matter below.
- Clarity and Focus: SMART objectives provide clear direction and allow individuals and teams to focus their efforts efficiently. They eliminate the ambiguity that can arise from vague objectives.
- Measurable Progress: Because SMART objectives are measurable, they allow for tracking progress over time. This can be motivating and can also highlight areas that need adjustment.
- Achievability: By ensuring that objectives are achievable, SMART criteria prevent setting goals that are too lofty and unrealistic, leading to frustration and demotivation.
- Relevance: Ensuring objectives are relevant means that effort and resources are directed towards goals that align with the broader mission and vision of the organization.
- Time Management: Time-bound objectives create a sense of urgency and a clear timeframe, which can aid in planning and prioritization.
- Improved Decision Making: With clear, measurable, and time-bound objectives, decision-making becomes more data-driven and aligned with the organization’s goals.
- Accountability: SMART objectives provide a clear benchmark for performance, making it easier to hold individuals or teams accountable for their outcomes.
Examples of Business Objectives
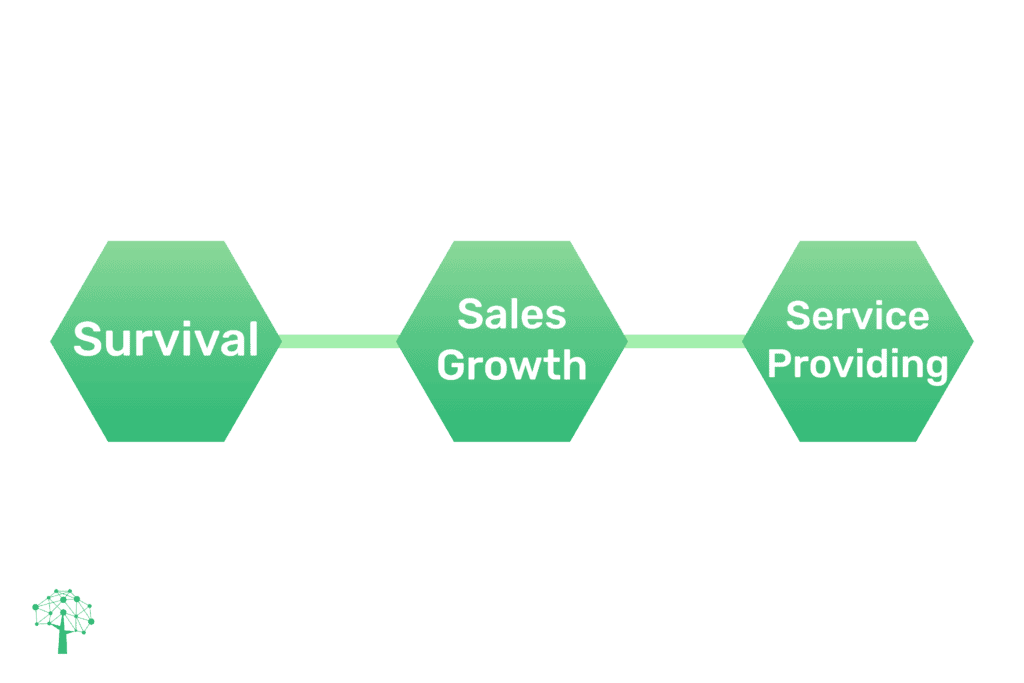
Here are some common objectives that both the private and public sector share:
Survival
This is a short-term objective that is usually set during times of crisis or when a small business is just starting. The objective of “survival” resembles an emergency alarm that requires serious and quick measures within tight deadlines. These types of objectives will immediately impact the business’s performance.
Sales Growth
As a matter of fact, in the world of business, money is the end goal of almost all businesses. It does not surprise that increasing the number of sales to the maximum is the objective of all companies, from start-ups to global businesses – sales growth is a common goal we all share.
Service Providing
This objective is more relevant to public sector organizations. Public services, like transportation, for example, do not have profit as their main focus. Their main objective is to provide value and facilitate the lives of the citizens. Even though these organizations gain some money, they must put the quality of the service itself before profit.
Business objectives examples for small business
Business objectives for small businesses are tailored to their specific needs, scale, and growth aspirations. Here are some examples of business objectives that a small business might set:
1. Sales and Revenue Objectives:
- Increase monthly sales by 15% over the next six months.
- Achieve a quarterly revenue of $50,000 by the end of the year.
2. Customer Acquisition and Retention:
- Acquire 100 new customers in the next three months.
- Reduce customer churn rate to below 5% for the next fiscal year.
- Increase repeat business from existing customers by 20% in the next quarter.
3. Market Expansion:
- Expand business operations to two new localities within the next year.
- Launch an online store and achieve 500 sales in the first six months.
4. Operational Efficiency:
- Reduce product return rates to below 3% by improving quality checks.
- Implement a new inventory management system to reduce stockouts by 50% within the next quarter.
5. Product and Service Development:
- Introduce two new product lines or services by the end of the year.
- Receive feedback from 80% of customers on a newly launched product within two months of its release.
6. Brand Awareness and Reputation:
- Increase social media followers by 30% over the next six months.
- Achieve a 4.5-star average rating on online review platforms by the end of the year.
7. Employee Objectives:
- Provide training programs for all employees to enhance their skills within the next quarter.
- Achieve an employee satisfaction rate of over 90% in the next survey.
8. Cost Management:
- Reduce operational costs by 10% in the next fiscal year through process improvements.
- Negotiate with suppliers to achieve a 5% reduction in raw material costs over the next six months.
9. Digital Presence and E-commerce:
- Increase website traffic by 40% in the next six months through SEO and content marketing.
- Achieve a conversion rate of 5% for online sales by optimizing the e-commerce checkout process.
10. Community Engagement and CSR:
- Organize quarterly community service events or workshops for the local community.
- Implement sustainable business practices to reduce the company’s carbon footprint by 20% next year.
When setting business objectives, small businesses, especially, should ensure that they are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to increase the likelihood of success and to facilitate performance tracking.
What is the Purpose of Aims and Objectives in Business?
Like many, you may be sceptical about setting objectives when starting a business. After all, aren’t the objectives of businesses pretty obvious? They want to make money, right? This is true, but it’s hardly the whole picture.
For one thing, ‘make lots of money’ isn’t the most concrete goal in the world, is it?
Your overarching mission might be to make a bundle of cash, but this is only half the story. When you define your business’s goals and objectives, you’re trying to create a roadmap to achieve profitability. Profitability is rarely possible without a clear definition of goals and objectives.
Why Businesses Set Aims and Objectives
Essentially, businesses set aims and objectives to give a framework for achieving success, as well as a way to monitor their progress. Your key business objectives should act as a guide for all of your staff throughout their daily tasks.
This has several benefits, including:
- Improving motivation and employee ownership of projects,
- Giving a clear mission,
- Helping your company to identify new ways to meet your core objectives.
Now that you know what aims, goals and objectives are for, let’s think more about how this influences your day-to-day operations.
What is the Difference Between Goals and Objectives in Business?
Business goals and objectives are not the same thing. As such, let’s look at what distinguishes business goals from how you define objectives.
This is pretty simple.
In short, your goals are your aspirations. They are what you’d like to achieve in a big-picture sense. By contrast, objectives are concrete deliverables to get you there.
Other Objectives
Ethical and Social Objectives
Some organizations and business entities look beyond profit. They aim to raise awareness towards a specific issue. Business owners usually set the tone for the issue the business is concerned with.
For example, some fashion houses aim to spread awareness about animal-friendly products that do not involve animal cruelty during manufacture. Sometimes, a business may choose to empower women or to erase illiteracy as their objective according to the nature of the business. Although these organizations are not charitable, they still select an ethical or social objective which benefits their community while making profits.
Charities and Voluntary Organizations
These non-profitable organizations do not care about profits, so their objectives are never financial. Their objectives usually target community development and accessible services to the less fortunate.
Additional Business Objectives
It may be easier to set out smaller objectives such as goals to achieve some of the larger-scale business objectives. These could include objectives per month, staff objectives and also the likes of organisation and risk objectives.

Revenue, ROI and Cost Objectives
All of these objectives involve the cost of the business or organisation. They also affect one another. Revenue is the amount of money a business or organisation makes in a particular period. It does not include costs of anything else, including production or staff costs.
These costs are deducted from the revenue to make up the business’s net income. Return on Investment known as ROI, is another cost. It should also be an objective set out by a business. This is calculated by including all costs and comparing them to the revenue made by a product or service. If a business fails to hit ROI business objectives/targets, staying afloat and surviving in the market may be difficult. Therefore, this objective is very important.
Other cost objectives may include efficiency. Efficiently includes factors such as ‘How many of a particular product can one staff member produce in a day?’ or ‘How many units of gas or electricity do I get with a certain amount of money?’. If these objectives aren’t met, it may be worth reconsidering the staff’s role or whatever company the business gets its electricity or gas from.
Product and Services
If a business’s products and services are not included in its objectives, there’s a problem. These need to be included in business objectives as the business will understand the future of their products and business.
There is no point in having a business objective of gaining more customers if you’re not offering more services or products that would interest more people. A business must also set new product and service objectives, such as development time, money to spend, and release date.
Customer and Employee Experience
Setting out business objectives for your employees and customers is also ideal. Examples of business objectives for customers would be upselling and cross-selling.
This allows the customer to gain more from their experience while also benefitting the business. Domino’s Pizza in the UK can be good at this via their app. Once someone has clicked to submit their order (depending on stores), it can then ask if they want to buy other products at a discounted rate.
This is good because Dominoes in the UK can be expensive, so getting a ‘deal’ would make the customer feel more satisfied with their order.
Business strategy types
Business strategy refers to the plans and actions businesses implement to achieve their goals and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Different business strategies cater to various aspects of a company’s operations, market positioning, and long-term vision. Here are some common types of business strategies:
1. Cost Leadership Strategy:
- This strategy aims to become the lowest-cost producer in the industry. By achieving economies of scale, optimizing operations, or sourcing cheap materials, companies can offer products or services at a lower price than competitors.
2. Differentiation Strategy:
- Companies using this brand development strategy aim to offer unique products or services that stand out from competitors. This uniqueness can be based on quality, design, features, customer service, or brand image.
3. Focused Cost Leadership:
- This strategy involves targeting a specific market segment and becoming the lowest-cost producer.
4. Focused Differentiation:
- Here, a company targets a specific market segment but offers unique products or services tailored to that segment’s needs.
5. Integrated Cost Leadership/Differentiation:
- Companies employing this strategy aim to use a mix of cost leadership and differentiation, offering unique products or services while maintaining competitive prices.
6. Growth Strategy:
- This strategy focuses on expanding the company’s footprint by increasing sales, entering new markets, or launching new products. Growth can be organic or through mergers and acquisitions.
7. Market Penetration Strategy:
- Companies aim to increase their market share in their current market, often by lowering prices, increasing advertising, or introducing minor product improvements.
8. Market Development Strategy:
- This involves entering new markets or targeting new segments with existing products.
9. Product Development Strategy:
- Companies focus on developing or upgrading new products to cater to their current market.
10. Diversification Strategy:
- This strategy involves entering entirely new markets with new products. It can be related (similar industry) or unrelated (different industry) diversification.
11. Retrenchment Strategy:
- When facing challenges, companies might reduce the scale of their operations by cutting down on expenses, selling off assets, or closing unprofitable business units.
12. Stability Strategy:
- Companies that are satisfied with their current position and performance might adopt a stability strategy, focusing on maintaining the status quo and making minor adjustments.
13. Blue Ocean Strategy:
- Instead of competing in saturated markets (red oceans), companies seek to create new market spaces (blue oceans) where competition is irrelevant, often by innovating or redefining industry boundaries.
14. Turnaround Strategy:
- Aimed at reversing a negative trend in a company, this strategy involves significant operational and strategic changes to recover from losses or declining performance.
Each business strategy type has its advantages and challenges. The choice of strategy often depends on the company’s current situation, industry dynamics, resources, and long-term vision. It’s also common for businesses to employ various strategies based on various factors and changing circumstances.
To Sum Up
Setting up business objectives and goals involves planning where your business is going. Objectives should be precise and clear. They explain to everyone the “how” of your business. Being transparent about your objectives with your employees and clients is a huge plus. How do we define business objectives?
According to the nature of the service or product you offer. Some objectives are obvious and common, like sales growth or improving services. The phase of the business also counts. A start-up’s objectives differ from an established business’s, even though they may meet at some point.
Finally, you can always seek a business consultant if unsure about your next objective. Explore the objectives of big companies and follow in their footsteps. There is always an area of development or a new objective to reach, so be creative and ambitious!
In short, how you set and define business goals and objectives will greatly impact all aspects of your company.
About ProfileTree

ProfileTree is a specialised marketing agency based in Belfast, Northern Ireland. We offer many specialist services to help you achieve your business goals and objectives. The internet is where your business now needs to be. Do you need a website, or do you already have one that isn’t working for you? We offer web design and development services that will enable you to understand the online market. If your website isn’t working, we can help with our SEO Marketing magic.
We also offer video production and development and social media marketing services, which could help your brand and business explode online. An online presence could be the last piece of the puzzle for reaching your business goals and objectives. To learn more about our services, visit our agency services page or contact one of our team members.


